ARM’s Cortex-A72 And Mali-T880 GPU Will Power Your 2016 Flagship Smartphones
ARM’s Cortex-A57 is just now starting to break stride with design wins and full-ramp production in new mobile products. However, today ARM is releasing a wealth of information on its successor: the Cortex-A72. ARM is targeting a core clock of 2.5GHz for the Cortex-A72 and it will be built using a 14nm/16nm FinFET+ process.
Using the Cortex-A15 (NVIDIA Tegra 4, Tegra K1) as a baseline, ARM says that the Cortex-A57 (Qualcomm Snapdragon 810, Samsung Exynos 5433) offers 1.9x the performance. Stepping up to the Cortex-A72, which will begin shipping in next year’s flagship smartphones, offers 3.5x the baseline performance of the Cortex-A15. These performance increases are being made within the same power envelope across all three architectures. So in turn, the Cortex-A72 can perform the same workload as the Cortex-A15 while consuming 75 percent less power.
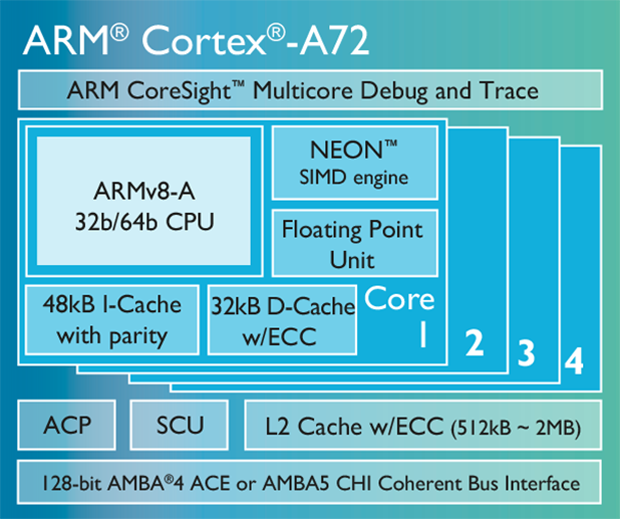
Much like the Snapdragon 810, which uses a big.LITTLE configuration (four low-power Cortex-A53 cores paired with four high performance Cortex-A57 cores), future SoCs using the Cortex-A72 will also be capable of big.LITTLE pairings with the Cortex-A53. According to ARM, allowing the Cortex-A53 to take care of mundane, everyday tasks while leaving high performance computing to the Cortex-A72 will allow for an additional 40 to 60 percent reduction in reduction in power usage when multitasking.
“Our new premium mobile experience IP suite with the Cortex-A72 processor delivers a decisive step forward from the compelling user experiences provided by this year’s Cortex-A57 based devices,” said Pete Hutton, executive vice president and president, products groups, ARM. “For multiple generations, together with our partners, we have delivered the leading-edge of the premium mobile experience. Building on this, in 2016 the ARM ecosystem will deliver even slimmer, lighter, more immersive mobile devices that serve as your primary and only compute platform.”
The performance and efficiency improvements of the Cortex-A72 can partially be attributed to the new CCI-500 north bridge. It offers twice the peak system bandwidth of the current generation CCI-400 while also offering up to a 30 percent increase in processor memory throughput. The CCI-500 north bridge will also play a key role in enabling 4K video capture at 120 fps.
Moving on, ARM has also announced its new Mali-T880 GPU, which offers 1.8x the performance of the current generation Mali-T760. Under identical workloads, the Mali-T880 offers a 40 percent reduction in power consumption compared to its predecessor. ARM again points to optimizations in the Mali-T880 to efficiently support 4K video playback.
ARM keeps touting power efficiency, and it does so for good reason. Smartphone processing performance has increased roughly 50x in the past five years. However, battery performance has only doubled during that same time. So every possible trick, or nip/tuck that will improve efficiency in today’s processors is key to keeping power consumption in check, especially with the rise of QHD displays (and the eventual 4K displays) and large-screen phablet devices.
That’s about it for now when it comes to the Cortex-A72, the CCI-500, and the Mali-T880. ARM says that it has already signed up partners including Rockchip, HiSilicon, and MediaTek (around a dozen in total so far). We’re hopeful that ARM will release more architectural details about Cortex-A72 as the year progresses, and if ARM and its partners stick to the planned schedule, we should start seeing products based on the new designs sometime next year.


