NVIDIA's PureVideo Technology
PureVideo Features (Cont.)

Bad Edit Detection (3:2 Correction)
Explanation - A further problem with video in 3:2 pull-down format is that post-conversion video editing can disrupt the normal 3:2 cadence. Basic inverse telecine solutions do not affect the deviation form. The resulting fields are used out of order so that every video frame displayed has jagged edge artifacts. NVIDIA PureVideo technology uses advanced processing to overcome the disrupted field sequence to display perfect picture detail frame after frame for smooth, natural looking video.
 NVIDIA GeForce 6600 GT |
 ATI Radeon X700 |
This pair of images also show a clear difference in each card's output. If you look closely at the truck's grill, between the '2' and the headlight, and along the edge of the windshield wipers, jaggies and feathering are visible in the frame captured with the Radeon that simply aren't there when using the GeForce 6600 GT with PureVideo. In conversations with representatives from ATI, however, they stated a software update would be able to address this issue.
Windows Media Video 9 Acceleration
Explanation - Microsoft's Windows Media Video 9 (WMV9) HD format was recently accepted by the SMPTE HD-DVD consortium as a new HD format. Windows Movie Maker software comes bundled with Windows XP to make it easy for consumers to edit and save their favorite videos. These videos are saved in the .WMV format. NVIDIA GeForce 6 Series GPUs is the first family of GPUs to include dedicated hardware to accelerate playback of WMV and WMV-HD content for fluid full frame rate video even on systems with entry-level CPUs. Previous generations of NVIDIA GPUs were not able to support WMV9 decode acceleration and often times HD WMV9 content would drop frames.
 NVIDIA GeForce 6600 GT |
 ATI Radeon X700 |
 NVIDIA GeForce 6600 GT (Patched) |
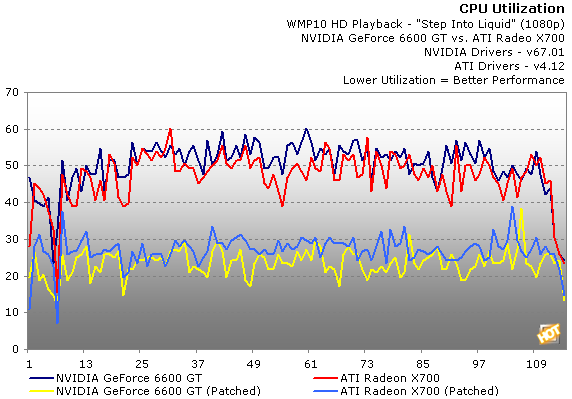
To document CPU utilization when playing back WMV HD content, we used the performance monitor built-into Windows XP. Using performance monitor, we created a log file that sampled the percent of CPU utilization every second, while playing back the 1080p version of the "Step Into Liquid" video available on Microsoft's WMVHD site. That data was then imported into Excel to create the graph above. The graph shows the CPU utilization for each card in an un-patched environment, as your system at home would be configured right now, and patched using a pair of DLLs supplied by NVIDIA. The updated files will be available in a patch to Windows Media Player 10, that should be released shortly.
With an un-patched system, CPU utilization was much higher during WMV HD playback. The Radeon had the overall advantage in the initial tests, but the GeForce 6600 was close behind. With the system patched, however, CPU utilization dropped significantly. This time around, the NVIDIA powered card had the slight advantage overall. Looking at the statistics below the graph, you can also see that each card performed similarly. In one instance, the 6600 dropped a single frame, but other than that there isn't much to point out. (Note: There is only one ATI statistics image, because the stats were identical in the patched and un-patched environments.)






